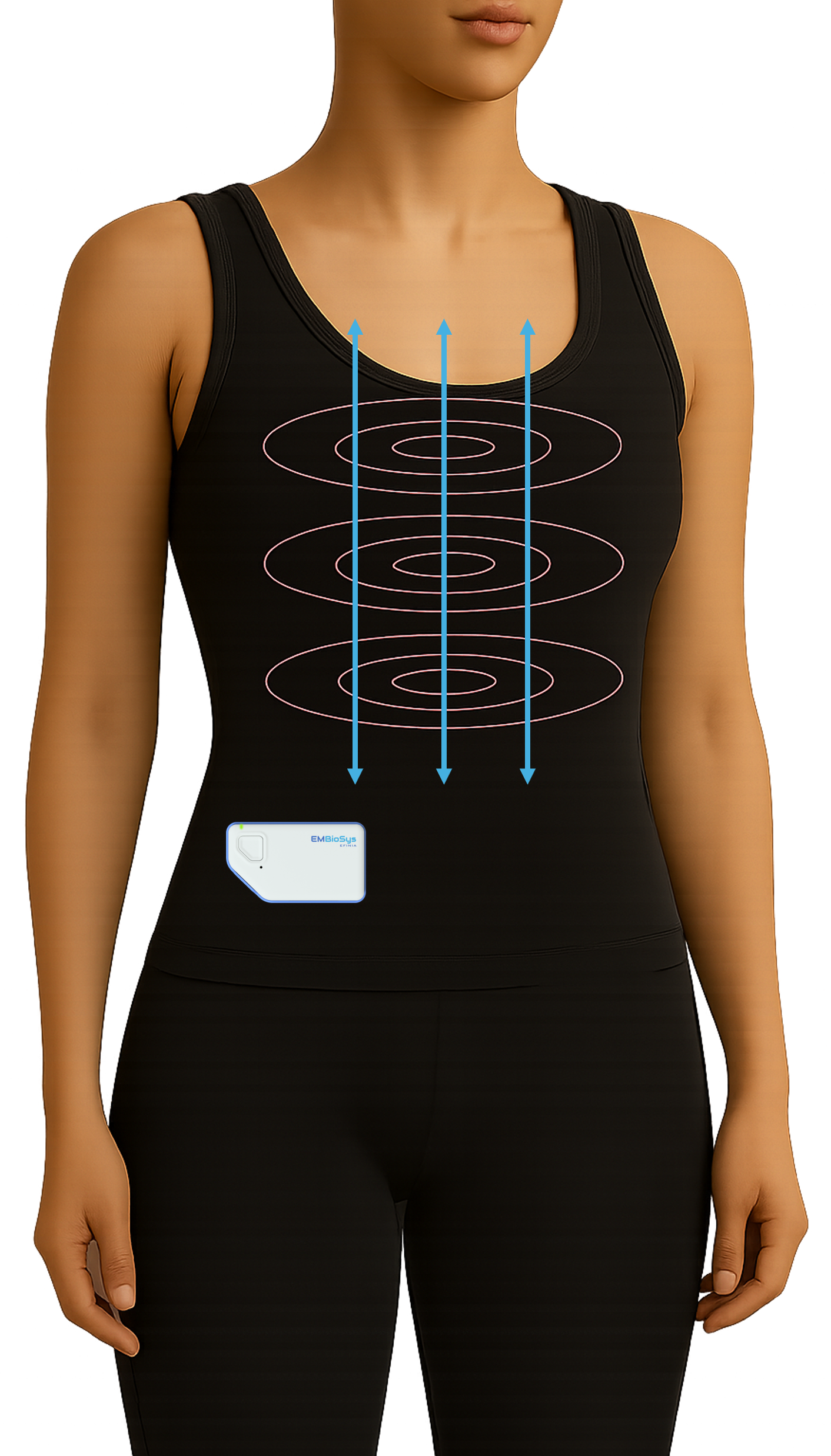
How Efinia™ works
Efinia™ works both at the cellular level targeting only cancer cells, and at the tissue, organ, and organism levels using a 4-pronged approach:
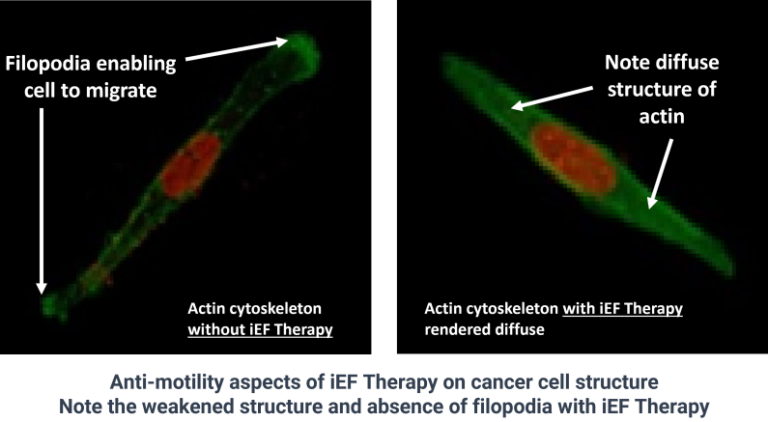
Cytoskeleton Disruption
Efinia™ alters the cancer cell's cytoskeleton making it unable to move
Metabolic Deprivation
Efinia™ metabolically deprive cells of energy to move and proliferate
Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) Reversal
Efinia™ reverses EMT preventing detachment
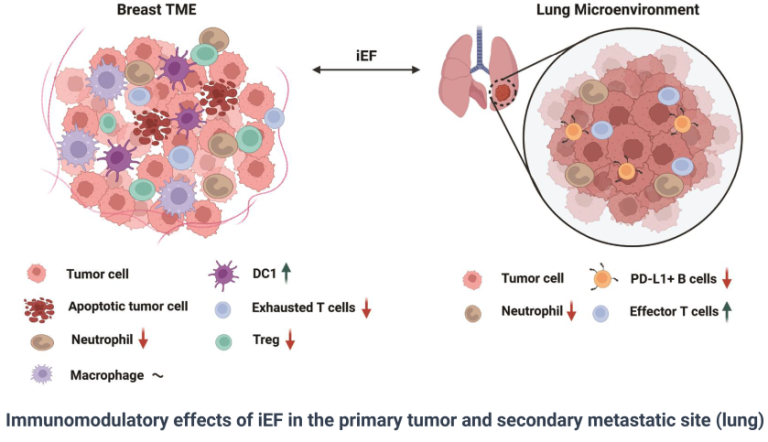
Immune Enhancement
Efinia™ boosts the immune system by attracting anti-tumor immune cells and dissuading pro-tumor immune cells
iEF Therapy Data
Pulmonary metastases are reduced
(in vivo – 4T1 model)
Tumor volume is reduced
(in vivo – 4T1 model)
Tumor weight is reduced
(in vivo – 4T1 model)
Source: Induced electric fields inhibit breast cancer growth and metastasis by modulating the immune tumor microenvironment; https://biorxiv.org/cgi/content/short/2024.04.14.589256v1
Anti-mobility effects of iEF Therapy
Immunomodulatory effects of iEF Therapy
“I am encouraged by the potential of induced Electric Field (iEF) Therapy as an innovative area of study for breast cancer. For decades, our approach to cancer treatment has rested on three fundamental pillars: surgery, systemic therapy, and radiation. The prospect of introducing a fourth modality—such as iEF Therapy—could be truly paradigm shifting, offering new hope for patients with difficult-to-treat cancers. I look forward to seeing how this technology may evolve and contribute to the future of oncology.”
- Dr. Sachin Jhawar, Radiation Oncologist
Publications
Induced electric fields inhibit breast cancer growth and metastasis by modulating the immune tumor microenvironment
Authors: Manish Charan, Travis H. Jones, Dinesh K. Ahirwar, Nandini Acharya, Vish V. Subramaniam, Ramesh K Ganju, and Jonathan W Song
Directional Migration of Breast Cancer Cells Hindered by Induced Electric Fields May Be Due to Accompanying Alteration of Metabolic Activity
Authors: Travis H. Jones, PhD, Kirti Kaul, PhD, Ayush A. Garg, PhD, Jonathan W. Song, PhD, Ramesh K. Ganju, PhD, and Vish V. Subramaniam, PhD
Electromagnetic fields alter the motility of metastatic breast cancer cells
Authors: Ayush Arpit Garg, Travis H. Jones, Sarah M. Moss, Sanjay Mishra, Kirti Kaul, Dinesh K. Ahirwar, Jessica Ferree, Prabhat Kumar, Deepa Subramaniam, Ramesh K. Ganju, Vish V. Subramaniam & Jonathan W. Song
Non-contact method for directing electrotaxis
Authors: Dinesh K. Ahirwar, Mohd W. Nasser, Travis H. Jones, Emily K. Sequin, Joseph D. West, Timothy L. Henthorne, Joshua Javor, Aniruddha M. Kaushik, Ramesh K. Ganju & Vish V. Subramaniam
Related Publications
Evaluation of electrical properties of ex vivo human hepatic tissue with metastatic colorectal cancer
Authors: Varun Lochab, Travis H Jones1, Emily Alkandryl, Joseph D Westl, Mohamed H Abdel-Rahman2, Vish V Subramaniam, and Shaurya Prakash
Ex vivo electrical impedance measurements on excised hepatic tissue from human patients with metastatic colorectal cancer
Authors: S. Prakash, M. P. Karnes, E. K. Sequin, J. D. West, C. L. Hitchcock, S. D. Nichols, M. Bloomston, S. R. Abdel-Misih, C. R. Schmidt, E. W. Martin Jr, S. P. Povoski, and V. V. Subramaniam